RotaChrom Technologies Unveils Laboratory-Scale Chromatographic Method Development Platform
Download, NewsFood & Beverages
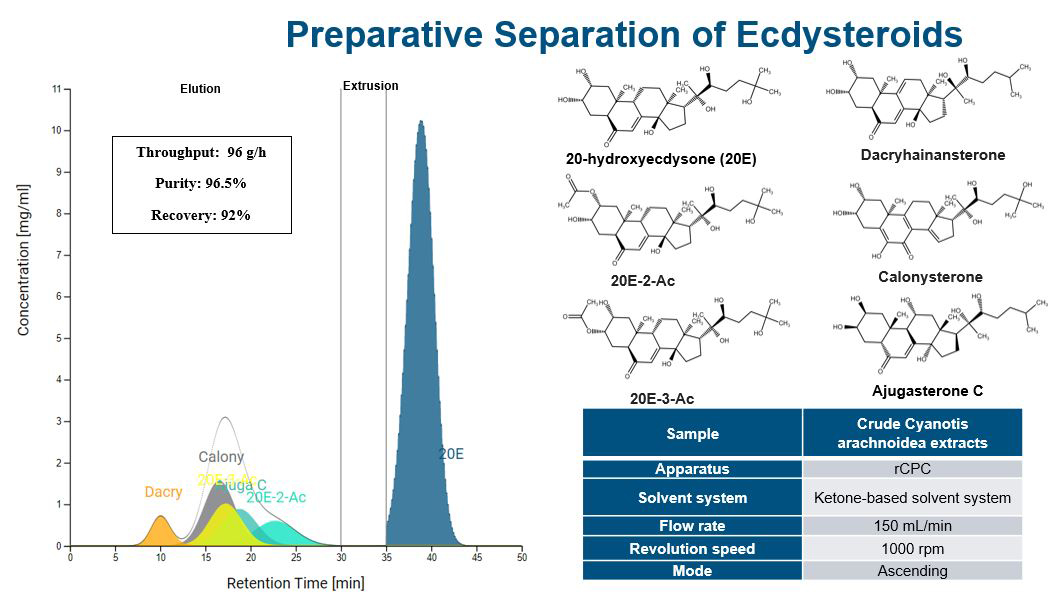
Preparative separation of ecdysteroids
Starting Material: Ecdysteroid-rich Cyanotis arachnoidea extracts
Goal: Isolation and purification
Ecdysteroids, abundant in plants, exhibit diverse pharmacological effects, including anabolic and neuroprotective properties. With growing demand for ecdysteroids in dietary supplements, there’s a clear need for industrial-scale isolation.
This study aimed to develop scalable centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC) methods for large-scale fractionation. The focus was on isolating 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E), the most abundant phytoecdysteroid, from Cyanotis arachnoidea extract used in supplements. Optimization of the CPC purification method yielded promising results: high stationary phase retention, solubility (>100 mg/mL), optimal distribution of target components (KD=0.5-2.0), and high selectivity (α >1.5). The optimized method proved simple, cost-effective, and scalable, achieving an impressive 80% isolated yield of 20E. Remaining minor and sub-minor ecdysteroids can be further fractionated using two-stage multiple dual-mode (MDM) methods, utilizing RotaChrom’s Continuous CPC. This research highlights CPC’s potential in industrial-scale ecdysteroid isolation, paving the way for advancements in pharmacology and dietary supplement production.
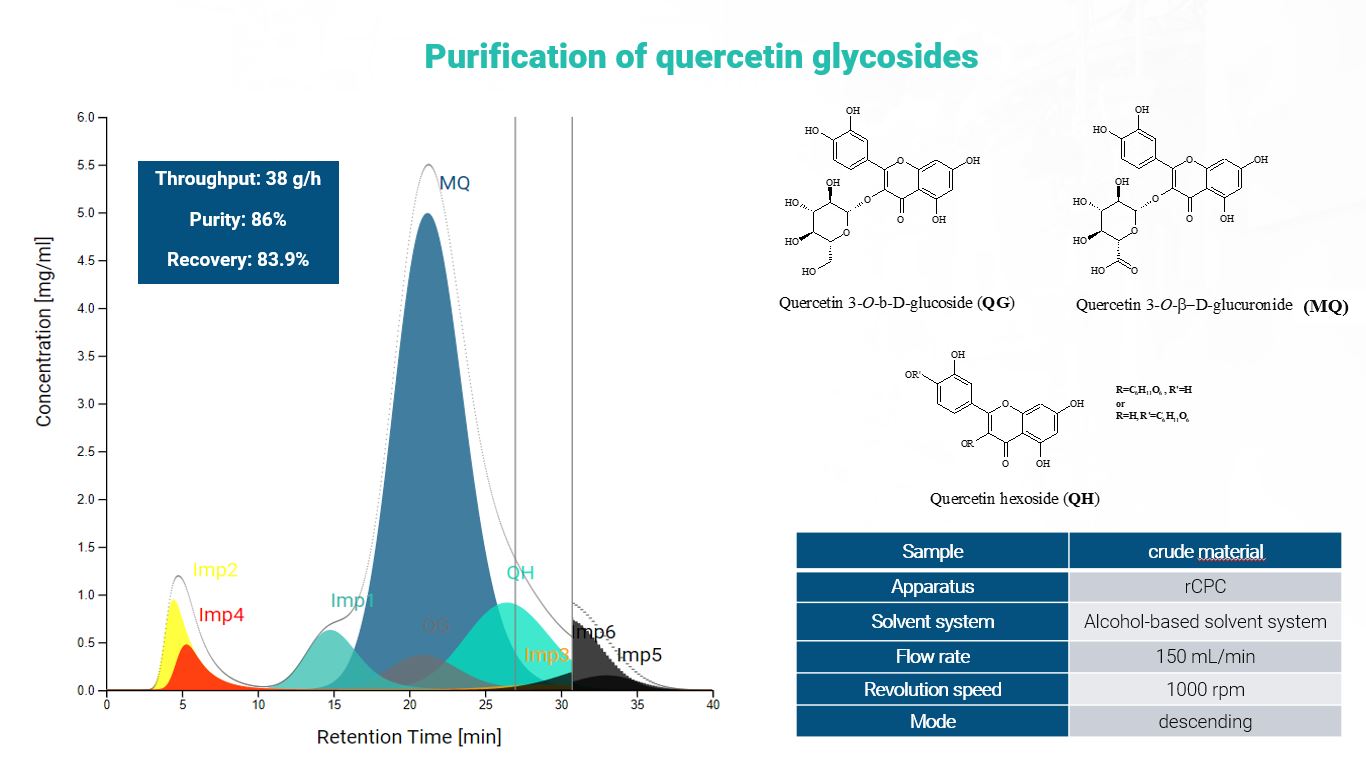
Purification of quercetin glycosides
Goal: Separation
The separation task was to investigate the feasibility of the isolation of quercetin glycosides. The primary objective was to achieve a purity value greater than 75% by weight for quercetin-3-β-O-D-glucoside (QG) quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronide (MQ) and a quercetin hexoside (QH) using food-grade solvents.
After extraction the developed CPC method was capable of isolating the three target compounds together with purity greater than the expected. It had a high throughput using only food grade chemicals. The end product could be re-crystallized from water which could further increase purity.
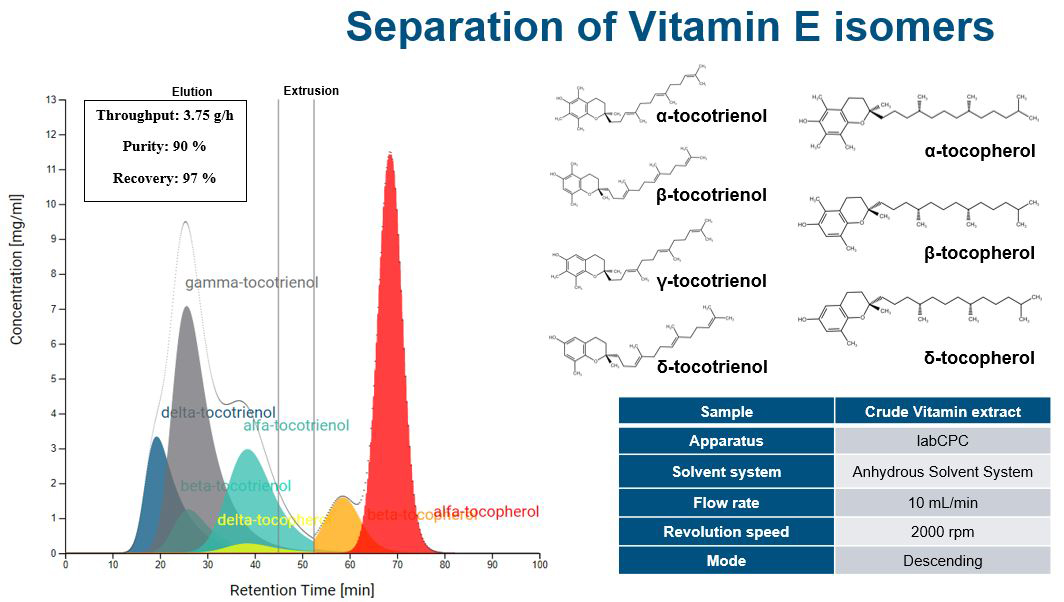
Separation of Vitamin E isomers
CoI: Tocotrienols and Tocopherols (members of the vitamin E family)
Goal: Separation
The oil included vitamin E isomers such as α-tocopherol, α-tocotrienol, β-tocopherol, β-tocotrienol, γ-tocotrienol, δ-tocopherol and δ-tocotrienol. Our CPC method could fractionate tocotrienols and tocopherols with excellent loading capacity: 50 ml injected volume to a 250 ml rotor. It achieved high selectivity for both the individual tocotrienols and tocopherols. The new method applied an anhydrous solvent system, which facilitated the recovery of the end product after the CPC run.
Contact us!
Latest News
Webinars
Contact Us
RotaChrom Technologies LLC (Headquarters)
Csillag street 2/A, Kecskemet, HU-6000
+36 70 885 6922
RotaChrom North America Inc.
300 Spectrum Center Drive, Irvine, CA 92618
+1 (720) 220-5669
Cookie Policy / Data Protection Policy / RotaChrom® is a registered trademark of Rotachrom Technologies in the USA and EU. / © 2024 RotaChrom Technologies. All rights reserved.
Application Library | RotaChrom Technologies LLC.