Increasing separation efficiency by pH adjustment in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography
NewsIn a recent NMR and chiroptical study related to kratom alkaloids, researchers used a RotaChrom CPC device.
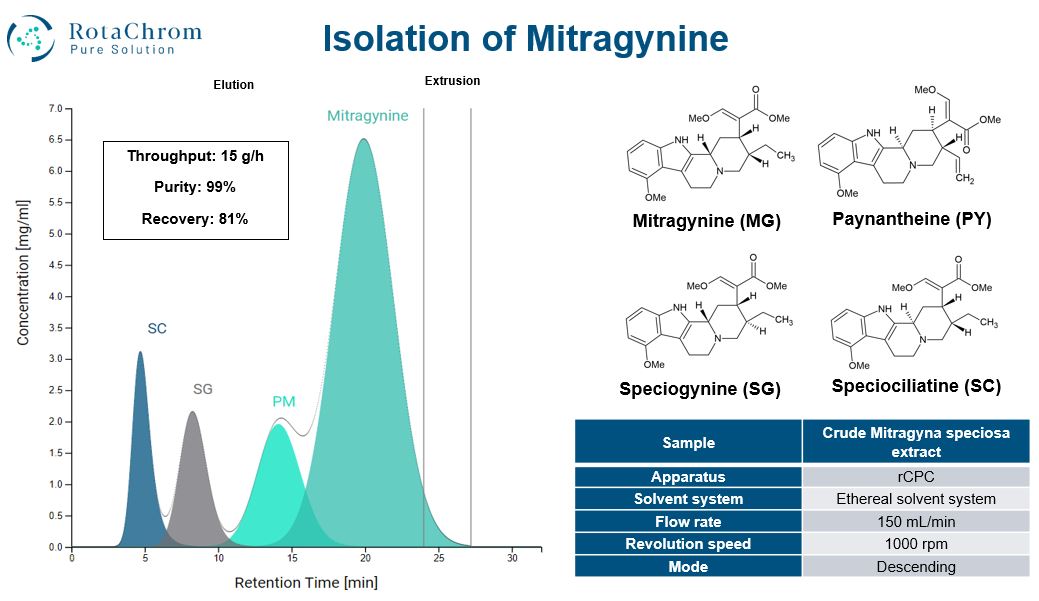
Mitragynine separation
Mitragynine (MTR) is a major alkaloid in Mitragyna speciosa leaf extract. It is a well-known plant commonly referred to as ‘kratom’. This plant is among the most studied botanical and natural products in recent memory, thanks to its notable biological effects. It is a partial agonist on the opioid receptors, and so it can relieve pain without the well-documented and understood side-effects of the currently used opioids in the clinical practice. Mitragynine and its derivatives are thus new candidates in drug research and development.
Kratom is indigenous to Thailand and Malaysia and is part of the Rubiaceae family. People in South Asia have used the plant’s leaf for hundreds of years to treat a variety of illnesses. Traditionally, people consume kratom in the form of tea, or even directly, chewing the freshly harvested leaves. The plant has stimulating and analgesic properties for which they are used regularly. In lower dosages, it offers energizing effects which can increase physical tolerance. Higher doses can produce adverse effects and can even produce withdrawal symptoms.
What makes mitragynine extraction challenging are the closely related alkaloids which are also present in the Mitragyna speciose leaf extract besides the main Compound of Interest (CoI), mitragynine. These other compounds include speciogynine (SG), speciociliatine (SC) and paynantheine (PM). The CoI needs to be separated from the surrounding alkaloids, which is a process that traditionally needs several steps.
Purifying mitragynine with CPC
It is a critical point when working with mitragynine to achieve a pure product which contains a large number of the Compound of Interest. Centrifugal Partition Chromatography is particularly suited for this goal. The researchers used a RotaChrom CPC device in the study which the company gifted to the laboratory: “MTR was isolated and purified by centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC) from kratom extract, and it was a generous gift from RotaChrom Ltd. (Dabas, Hungary). Native βCyD and randomly substituted SBEβCyD (DS ~ 6.5) were the products of CycloLab Ltd. (Budapest, Hungary). D2O (99.9 atom% D) was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), while acetic acid-d4 was obtained from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories Inc (Tewksbury, MA, USA). Other base chemicals of analytical grade were from commercial suppliers and used without further purification”.
RotaChrom’s pilot-scale device, the rCPC can isolate mitragynine from samples up to 99% purity. And it can do it cost-effectively compared to traditional purification techniques. RotaChrom’s novel solution can purify mitragynine directly from the crude extract in a few steps and in an economical way.
Click here if you would like to learn more about our CPC technology.
Conclusion and Outcomes
The research yielded promising results: “In the present study, interactions of MTR with CyDs were characterized extensively by NMR and CD spectroscopy. 1H NMR titration studies revealed a weak (logb11 = 0.8; MTR0 CyD) binding between MTR and CyD, while in the case of SBE CyD a much stronger interaction was identified (logb11 = 3.68, logb21 = 6.87). For the latter case, the co-existence of 1:1 and 2:1 MTR-SBE CyD complexes was deduced.
The CD titration experiments yielded a Kd of 206 M, which is in a good agreement with the NMR spectroscopic results. Furthermore, the Hill coefficient (>1) also suggested the prevalence of complexes exceeding the simple 1:1 stoichiometry. Sulfobutylation of CyD yielded a 750-fold increase in supramolecular stability due to the enlarged cavity, sidechain flexibility, and the possibility of host-guest electrostatic interaction.
The structure of the complex was proposed based on CD and NMR data. Both techniques revealed the insertion of the indole moiety into the CyD cavity. Moreover, some NMR and CD spectral signatures were described herein, which are characteristic to the MTR-CyD complex formation. As such, they could be utilized in the future for detection and evaluation of various inclusion complexes of structurally related indole and oxindole kratom alkaloids.”
Want to get in touch?
Fill in the form below so our representatives can contact you. We will also let you in on more information on our technology.