Increasing separation efficiency by pH adjustment in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography
NewsManufacturing small molecule Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) is a complex process that requires specialized facilities, regulatory experience, chemistry expertise, and supply chain management. To meet these challenges, many pharmaceutical innovators turn to CDMOs (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations) to produce their APIs. To produce high purity pharmaceutical products, it is essential to have a robust and effective process for manufacturing APIs or key intermediates. Depending on the characteristics of the product and the nature of the process, various techniques may be utilized. One commonly used method is preparative chromatography, which is effective for separating, purifying, and isolating substances from complex mixtures.
Manufacturing APIs
APIs are the biologically active substances that are found in medicinal products. They are the active ingredients that are responsible for the desired therapeutic effect of the medication. APIs can be derived from a variety of sources, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, and they can be produced through a variety of methods, including chemical synthesis and fermentation.
APIs are typically formulated into finished dosage forms, such as tablets, capsules, and injections, which are then distributed to patients. However, APIs can also be supplied as standalone products to other pharmaceutical manufacturers, who may use them to formulate their own finished dosage forms.
The production of APIs is a highly regulated process, as the purity and quality of the active ingredient is critical to the safety and effectiveness of the final medicinal product. APIs must meet strict quality standards, and the manufacturing process must be carefully controlled to ensure that the final product is consistent and meets the required specifications.
In addition to quality control, the production of APIs also requires careful consideration of other factors, such as yield, cost, and scalability. As APIs are typically produced in large quantities, it is important to develop an efficient and cost-effective manufacturing process that can be scaled up to meet demand.
CDMOs
Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) are companies that provide services related to the development and manufacturing of pharmaceutical products. These services may include research and development, process development and optimization, analytical testing, quality control, regulatory affairs, and manufacturing.
CDMOs are often used by pharmaceutical companies that do not have the internal resources or capabilities to develop and manufacture their own products, or that want to outsource certain aspects of the development and manufacturing process to focus on other areas of their business. CDMOs can provide expertise and support throughout the development process, from early stage research and development to late stage clinical trials and commercial manufacturing.
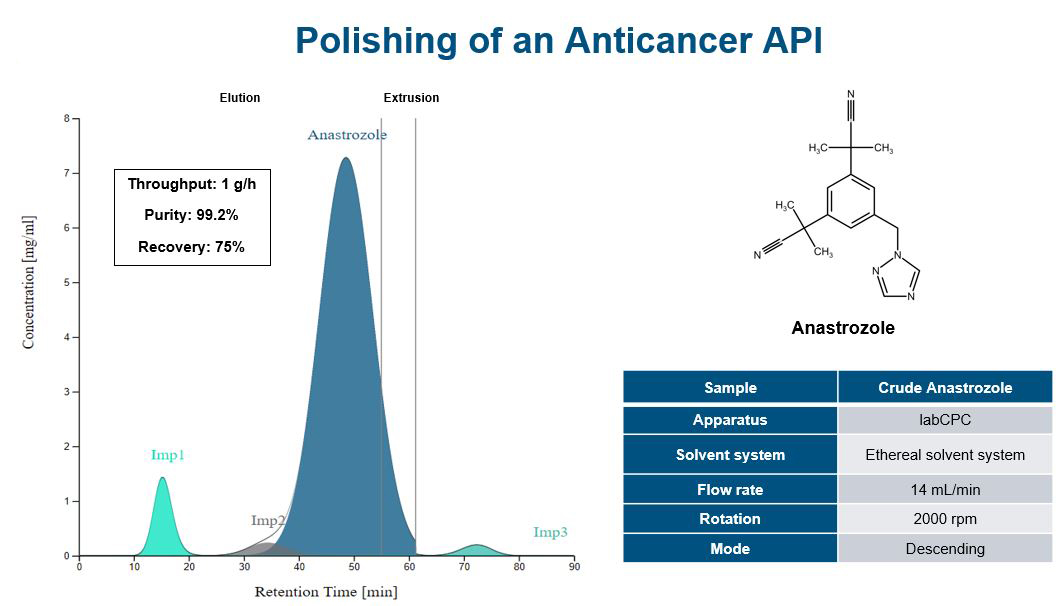
Producing APIs with RotaChrom
RotaChrom has developed a groundbreaking method for preparative purification called Industrial-Scale Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Unlike traditional methods that rely on a solid stationary phase, RotaChrom’s technology uses a liquid-liquid approach to achieve precise molecular separation. The result is a system that is superior in terms of yield and purity, and also reduces costs and simplifies downstream method development for a wide range of purification tasks.
This novel CPC technology does not need any silica gel to operate. Liquid-liquid chromatography is a chromatographic separation method where both the mobile and stationary phases are liquids. It integrates the principles of liquid-liquid separation and chromatography. In this system, the separation occurs between two immiscible liquid phases. The basis for the separation is the differential partitioning of solutes between the two phases.
In LLC, just like in traditional chromatographic separation methods, one of the phases involved acts as the stationary phase. The liquid stationary phase is maintained in place during the separation process by a strong centrifugal force. The advantage of this system is the ability to load high sample volumes, as the solutes can access the entire volume of the liquid stationary phase. Furthermore, liquid-liquid chromatography eliminates the issue of irreversible adsorption, allowing for complete sample recovery.
Our technology can be used for a wide range of applications, including the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, natural extract and cosmetic and fragrance industries. RotaChrom’s CPC system has almost no limit on adaptation from small molecule APIs to macromolecules or from hydrophobic lipids to completely hydrophilic peptides on the same instrument. RotaChrom instruments are also capable of separation, isolation and remediation tasks (the pCPC can even do all 3 as a single platform).
If you would like to see real life examples of how you can utilize CPC in your purification goals, click here to take a look at RotaChrom’s application library.



