Increasing separation efficiency by pH adjustment in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography
NewsIn this series, we look at the main aspects of chromatography. We started with the basics and now we begin to work our way towards more complex topics, such as Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Our goal is to make chromatography easy to understand, so that anyone can get a grasp of the subject. Last time we learnt about the downstream process, and the core elements of chromatography. We also learnt how the basics can be modified and utilized to achieve certain goals. This week we will learn about the chromatogram and chromatographic optimization.
Are you a chromatography expert already? If so, we have more advanced resources for you. Click the green button if you are interested!
The Chromatogram
In short, the chromatogram is the visual output of the chromatographic system. It is essentially a graph that shows the events of a particular chromatographic process:
- The Y axis is the detection response of a particle.
- The X axis is the time of the separation process.
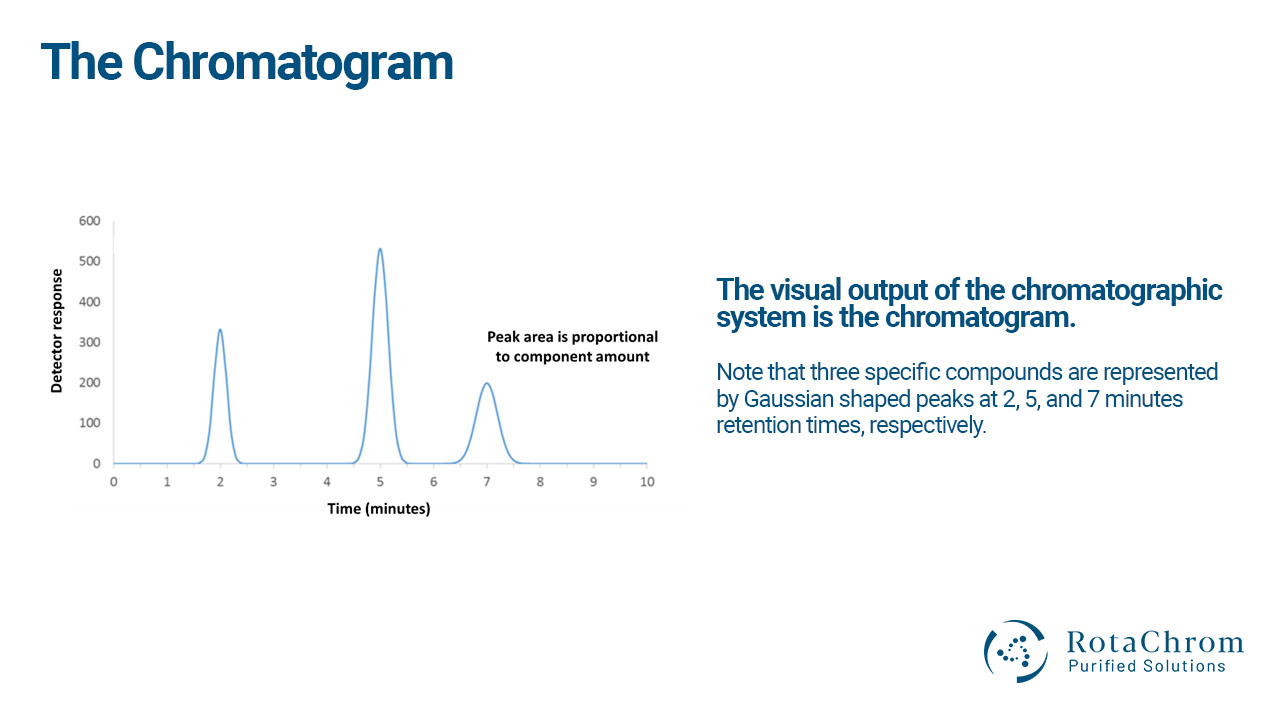 It is important to understand how to read a chromatogram. There are several questions that it can answer, which provides valuable input about the details of a specific process:
It is important to understand how to read a chromatogram. There are several questions that it can answer, which provides valuable input about the details of a specific process:
What does a peak show?
- Each peak of the Gaussian shapes show a different type of separated compound.
What is the amount of a compound in the mixture during a peak?
- The area under the Gaussian curve is proportional to the amount of the compound.
Where is the peak?
- It shows when and in which fraction the elution happens, and the distance and separation of the peaks show selectivity and purity.
As mentioned many times in our articles, the goal of a chromatographic separation is achieving resolution. In a chromatogram, resolution is visualized by peaks that have no overlap between them. Higher resolution (no overlap) means the separation was successful. This results in a purer product. The value of the resolution is marked with ‘Rs’ in a chromatogram.
Overlapping peaks do not have great resolution. An Rs value lower than 1.5 means the peaks in the chromatogram are overlapping. On the other hand, if the Rs value is higher than 1.5, means you achieved ‘baseline separation’, which is the ‘Holy Grail’ of chromatography so to say. Baseline separation results in no overlapping peaks at all.
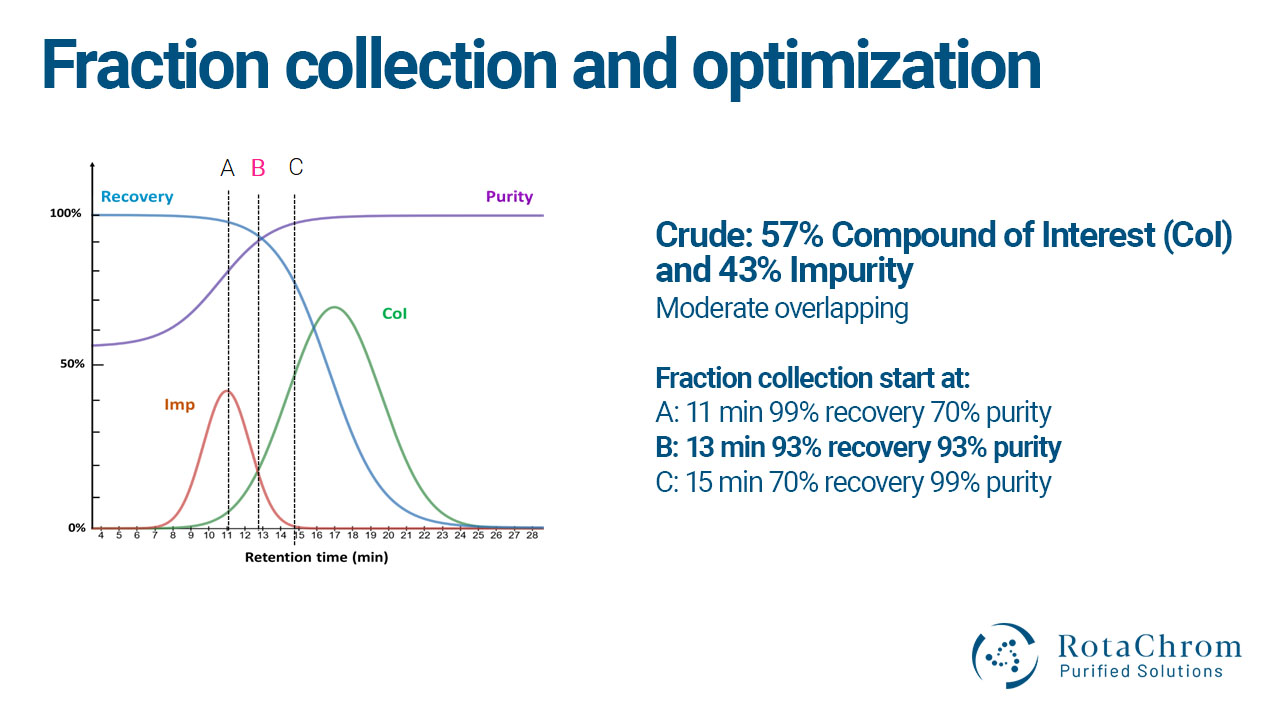
Fraction collection and optimization
As defined earlier in our articles, the goal of chromatographic remediation is to separate impurity from a Compound of Interest (CoI). Impurity can be many different things, including a health threat, a carcinogen, an environmental pollutant, or a legally challenging compound among others. Problems can arise, however, if the impurity that you want to remove comes out around the same time the CoI you want to separate starts to come out. This is an obvious issue, and in such cases, you need to optimize the chromatographic process and take into account that there is going to be some tradeoff between purity and recovery. If that is the case, you need to decide which is more important for your purposes: purity or recovery.
- The more impurity you remove, the less sample you can recover
- The more sample you recover, the less pure it is
Achieving optimal balance
Engineers and scientists have been working on methods to balance the purity-recovery gap. The idea is, that if you start the collection at the right time, you can balance between the two extremes, and aim for optimum recovery and purity. This is how you strike a “sweet-spot” between losing some of the material (but not much), and still achieving very high purity.
Many different chromatographic methods exist to apply the most selective and most efficient method to get rid of contamination, heavy metals, pesticides. For example, our engineers at RotaChrom developed a revolutionary device called the Industrial Scale Centrifugal Partition Chromatographic (iCPC) device.
RotaChrom’s system doesn’t use any solid stationary phase (e.g. silica gel). It has been shown to be superior to conventional liquid chromatographic techniques in terms of yield and purity. In addition, the iCPC platform has radically reduced the costs and number of steps associated with downstream method development for a diverse array of purification challenges.
In the future, we will go into much more detail about Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. But if you’re curious, take a look at RotaChrom’s Technology page which will give you a head-start in the topic.
Want to get in touch?
Fill in the form below so our representatives can contact you. We will also let you in on more information on our technology.