SZTE’s Award-Winning Innovation: A Natural Breakthrough in Obesity Prevention
Education, News, StudiesIn this series, we continue to look at the main aspects of chromatography. Our first article introduced the basics. Then last time we looked at the chromatogram and optimizing the process. We are now working our way up towards more complex topics, such as Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Our goal is to make chromatography easy to understand, so that anyone can get a grasp of the subject. This time, we are looking at the differences between analytical vs preparative chromatography, so that we can finally dive into Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. But more on that in the next article.
Are you a chroamtography expert already? If so, we have more advanced chromatography resources available for you already! Click the button below to read more.
Analytical vs preparative chromatography
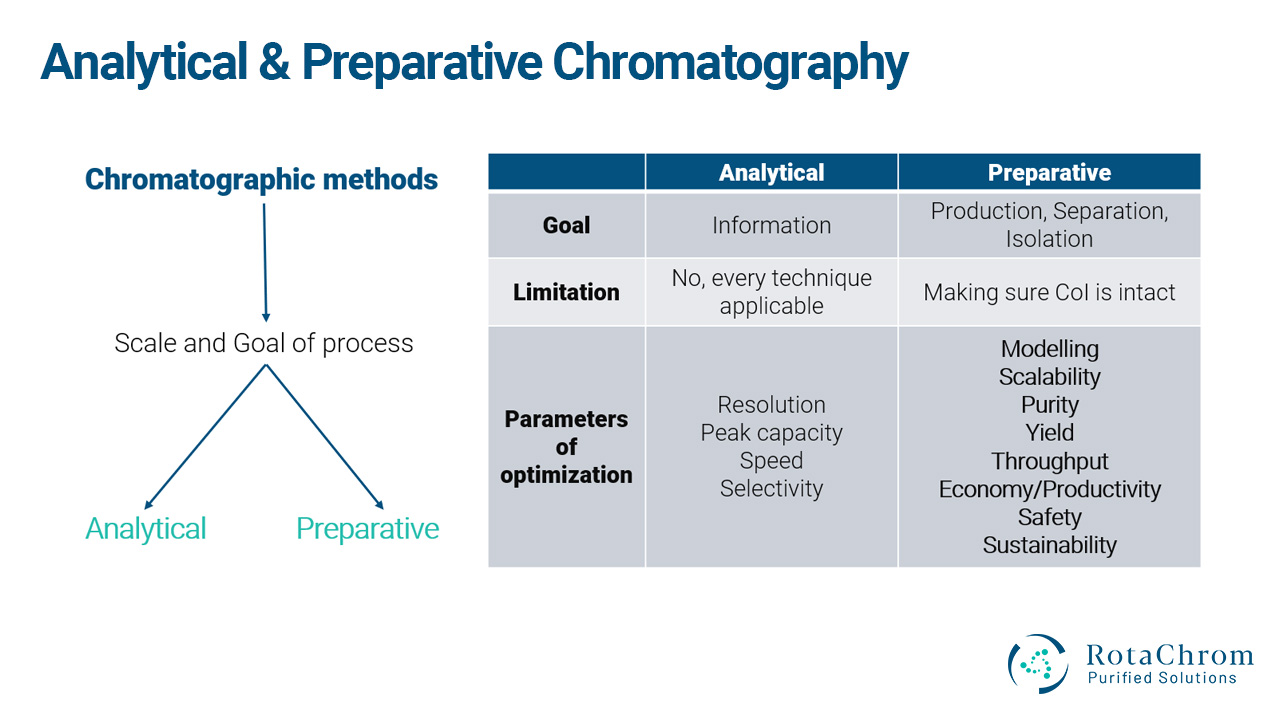
Chromatographic methods can be classified into analytical and preparative ones based on the scale and the goal of the separation process. In the case of analytical methods, the aim of the separation is to achieve qualitative and quantitative information about the sample in question.
On the other hand, the goal of preparative separations is to isolate a specific component of a mixture (called the compound of interest, abbreviated as CoI) or otherwise remediate a single component or group of components (impurity or impurities) from the mixture. These preparative systems are capable of processing hundreds or even thousands of grams of input.
 So, to recap:
So, to recap:
Analytical:
- In the case of analytical methods, the aim of the separation is to obtain qualitative and quantitative information about the sample .
- Analytical is smaller scale. It is mainly for information and research.
Preparative:
- Larger scale.
- It can process substantial amounts.
- The goal is to isolate a specific compound from a mixture (i.e., the CoI) or alternatively remove a single compound or group of compounds (i.e., impurity or impurities) from the mixture.
- Preparative systems can process hundreds or even thousands of grams of input material and work in the multi-liter per minute flow rate range.
Industrial-scale purification
As a next step of preparative chromatography, it is important we touch on industrial-scale chromatography. To explain the concept, we would like to talk about the iCPC, RotaChrom Technology’s flagship Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC) device.
Like conventional liquid chromatography, separation of the injected sample is based on the sample component’s varying partition coefficients between the mobile and stationary phases. The partition coefficient dictates the amount of time each molecule spends within the mobile and stationary phases and therefore the rate at which each molecule travels through the system. At the end of the purification process automated fraction collectors retain all selected fractions based on the program settings.
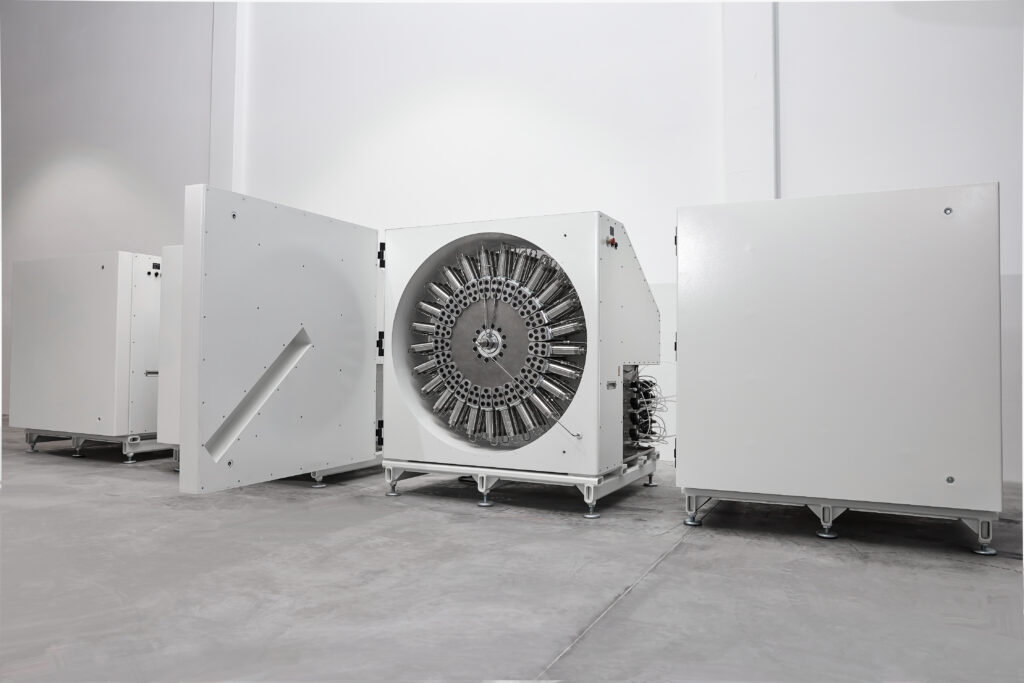 RotaChrom’s iCPC platform is the largest commercially available Centrifugal Partition Chromatography instrument in the world. Designed for industrial-scale purification projects in continuous batch operation mode, this device is by far the most cost-effective industrial-scale chromatography platform available on the market. It has the capacity to process hundreds of kilograms of crude input material per month.
RotaChrom’s iCPC platform is the largest commercially available Centrifugal Partition Chromatography instrument in the world. Designed for industrial-scale purification projects in continuous batch operation mode, this device is by far the most cost-effective industrial-scale chromatography platform available on the market. It has the capacity to process hundreds of kilograms of crude input material per month.
In the future, we will go into much more detail about Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. But if you’re curious, take a look at RotaChrom’s Technology page which will give you a head-start in the topic. Or if you’re interested in more in-depth topics related to chromatography, or would like to follow along with this series, make sure to follow RotaChrom on LinkedIn and bookmark our News page!
Want to get in touch?
Fill in the form below so our representatives can contact you. We will also let you in on more information on our technology.